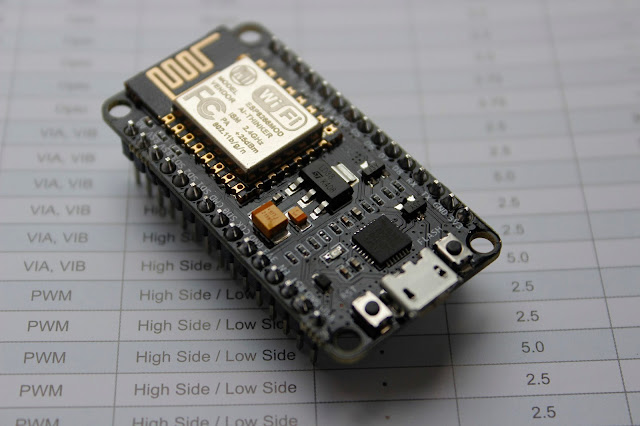
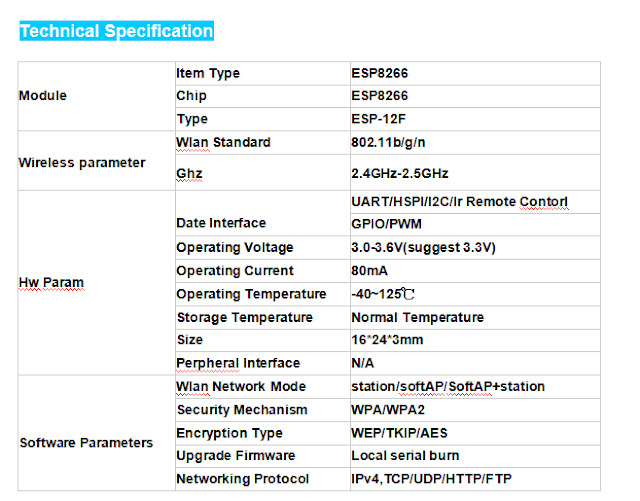
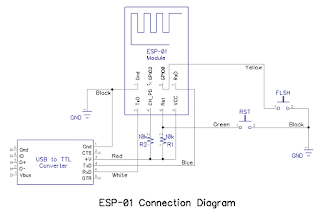
ESP8266 series module developed by Ai-thinker adopts Espressif ESP8266 chip.
ESP8266 特性:
*802.11 b/g/n
*内置低功耗32位CPU:可以兼作应用处理器
*内置10 bit高精度ADC
*内置TCP/IP协议栈
*内置TR开关、balun、LNA、功率放大器和匹配网络
*内置PLL、稳压器和电源管理组件
*支持天线分集
*STBC、1x1 MIMO、2x1 MIMO
*A-MPDU、A-MSDU的聚合和0.4 s的保护间隔
*WiFi @ 2.4 GHz,支持 WPA/WPA2 安全模式
*支持STA/AP/STA+AP工作模式
*支持Smart Config功能(包括Android和iOS设备)
*SDIO 2.0、(H) SPI、UART、I2C、I2S、IR Remote Control、PWM、GPIO
*深度睡眠保持电流为10 uA,关断电流小于5 uA
*2 ms之内唤醒、连接并传递数据包
*802.11b模式下+20 dBm的输出功率
*待机状态消耗功率小于1.0 mW (DTIM3)
*工作温度范围:-40°C - 125°C
*通过 FCC, CE, TELEC, WiFi Alliance 及 SRRC 认证
ESP8266 Feature:
*802.11 b/g/n protocol
*Wi-Fi Direct (P2P), soft-AP
*Integrated TCP/IP protocol stack
*Integrated TR switch, balun, LNA, power amplifier and matching network
*Integrated PLL, regulators, and power management units
*+19.5dBm output power in 802.11b mode
*Supports antenna diversity
*Power down leakage current of < 10uA
*Integrated low power 32-bit MCU
*SDIO 2.0, SPI, UART
*STBC, 1x1 MIMO, 2x1 MIMO
*A-MPDU & A-MSDU aggregation & 0.4μs guard interval
*Wake up and transmit packets in < 2ms
*Standby power consumption of < 1.0mW (DTIM3)
超低功耗技术:
ESP8266EX专为移动设备、可穿戴电子产品和物联网应用设计,并与其他几项专利技术一起使机器实现 最低能耗。这种节能的构造以三种模式运行:激活模式、睡眠模式和深度模睡眠式。
ESP8266EX使用高端电源管理技术和逻辑系统调低非必需功能的功率,调控睡眠模式与工作模式之间的 转换,在睡眠模式下,其消耗的电流小于12 uA,处于连接状态时,其消耗的功率少于1.0 mW(DTIM=3) 或 0.5 mW (DTIM = 10)。
睡眠模式下,只有校准的实时时钟和watchdog处于工作状态。可以通过编程使实时时钟在特定的时间 内唤醒 ESP8266EX。
通过编程,ESP8266EX会在检测到某种特定情况发生的时候自动唤醒。ESP8266EX在最短时间内自动 唤醒,这一特征可以应用到移动设备的SOC上,这样SOC在开启Wi-Fi之前均处于低功耗待机状态。
为满足移动设备和可穿戴性电子产品的功率需求,ESP8266EX在近距离时可以通过软件编程减少PA的输 出功率来降低整体功耗,以适应不同的应用方案。
Ultra Low Power Technology:
ESP8266EX has been designed for mobile, wearable electronics and Internet of Things applications with the aim of achieving the lowest power consumption with a combination of several proprietary techniques. The power saving architecture operates mainly in 3 modes: active mode, sleep mode and deep sleep mode.By using advance power management techniques and logic to power-down functions not required and to control switching between sleep and active modes, ESP8266EX consumes about than 60uA in deep sleep mode (with RTC clock still running) and less than 1.0mA (DTIM=3) or less than 0.5mA (DTIM=10) to stay connected to the access point.
When in sleep mode, only the calibrated real-time clock and watchdog remains active. The real-time clock can be programmed to wake up the ESP8266EX at any required interval.
The ESP8266EX can be programmed to wake up when a specified condition is detected. This minimal wake-up time feature of the ESP8266EX can be utilized by mobile device SOCs, allowing them to remain in the low-power standby mode until Wi-Fi is needed.In order to satisfy the power demand of mobile and wearable electronics, ESP8266EX can be programmed to reduce the output power of the PA to fit various application profiles, by trading off range for power consumption.
主要应用领域:
智能家居
家庭自动化
智能插座、智能灯
网状网络
工业无线控制
婴儿监控器
网络摄像机
传感器网络
可穿戴电子产品
无线位置感知设备
安全ID标签
无线定位系统信号
ESP8266EX Applications
*Smart power plugs
*Home automation
*Mesh network
*Industrial wireless control
*Baby monitors
*IP Cameras
*Sensor networks
*Wearable electronics
*Wi-Fi location-aware devices
*Security ID tags
*Wi-Fi position system beacons
ESP8266系列模块现在主要包括以下类型:
ESP-01 包括两个版本,一个是篮色版,一个是黑色版本的,功能一样,Pin脚一样,只是主板颜色不同,蓝色是老版产品,目前AI-thinker已经停产这种版本,但是市场上还是有一些在售产品,后期ESP-01都是黑色版本的。ESP-01 共接出 8 个接口 ,ESP-01 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为14.3mm*24.8mm*3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。模组使用的是3 DBi 的PCB 板载天线。
ESP8266 series modules As following types:
ESP - 01 includes two versions, one Blue version and a black version, functions and Pin is same, only the mainboard.it is different the color of mainboard . the AI - thinker have shut down Blue version now, ESP-01 are altogether 8 pin counts, The external size of the module is 14.3mm*24.8mm*3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
The antenna applied on this module is a 3DBi PCB-on-board antenna.
ESP-02 共接出8个接口,ESP-02 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 14.9mm*16.3mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。
ESP-02 are altogether 8 pin counts, The external size of the module is 14.9mm *16.3 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
ESP-03 共接出 14个接口,ESP-03 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为17.3mm*12.1mm*3mm。该模组采用的是容量为1MB, 封装为SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。模组使用的是陶瓷板载天线。
ESP-03 are altogether 14 pin counts, The external size of the module is 17.3mm *12.1 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
The antenna applied on this module is a ceramic antenna.
ESP-04 共接出14个接口,ESP-04 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 14.7mm*12.1mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。
ESP-04 are altogether 14 pin counts, The external size of the module is 14.7mm *12.1 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
ESP-05 共接出 5个接口,ESP-05 贴片式模组的外观尺为 14.2mm*14.2mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。
ESP-05 are altogether 5 pin counts, The external size of the module is 14.2mm *14.2 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
ESP-06共接出 20个接口,ESP-06E 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 16.2mm*13.2mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。
ESP-06 are altogether 5 pin counts, The external size of the module is 16.2mm *13.2 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
ESP-7共接出16个接口,ESP-07 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 16mm*21.2mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。配有陶瓷天线。
ESP-07 are altogether 5 pin counts, The external size of the module is 16mm *21.2 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
The antenna applied on this module is a ceramic antenna.
ESP-08共接出16个接口,ESP-08 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 16mm*18.5mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。
ESP-08 are altogether 5 pin counts, The external size of the module is 16mm *18.5 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
ESP-09共接出 20个接口,ESP-09 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 10mm*10mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。
ESP-09 are altogether 20 pin counts, The external size of the module is 10mm *10 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
ESP-10共接出 5个接口,ESP-10 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 16mm*18.5mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。
ESP-10 are altogether 5 pin counts, The external size of the module is 16mm *18.5 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
ESP-11共接出 8个接口,ESP-11 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 16mm*18.5mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 1MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。
ESP-11 are altogether 8 pin counts, The external size of the module is 16mm *18.5 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 1 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
ESP-12 共接出16 个接口,ESP-12 贴片式模组的外观尺?寸为 16mm*24mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 4MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。模组使用的是 3 DBi 的 PCB 板载天线。
ESP-12 are altogether 18 pin counts, The external size of the module is 16mm *18.5 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 4 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
The antenna applied on this module is a 3DBi PCB-on-board antenna.
ESP-12E 共接出 22 个接口,ESP-12E贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 16mm*24mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 4MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。模组使用的是 3 DBi 的 PCB 板载天线。
ESP-12E are altogether 16 pin counts, The external size of the module is 16mm *24 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 4 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
The antenna applied on this module is a 3DBi PCB-on-board antenna.
ESP-12F 共接出 22个个接口,ESP-12F 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为 16mm*24mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 4MB, 封装为 SOP-210 mil 的 SPI Flash。模组使用的是 3 DBi 的 PCB 板载天线。
ESP-12F are altogether 18 pin counts, The external size of the module is 16mm *24 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 4 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
The antenna applied on this module is a 3DBi PCB-on-board antenna.
ESP-13 共接出 18 个接口,ESP-13 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为18mm*20mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为 4MB, 封装为 SOP-150 mil 的 SPI Flash。模组使用的是 3 DBi 的 PCB 板载天线。
ESP-13 are altogether 18 pin counts, The external size of the module is 18mm *20 mm *3mm .The type of Flash integrated in this module is an SPI flash, the capacity of which is 4 MB,the package size of which is SOP-210mil.
The antenna applied on this module is a 3DBi PCB-on-board antenna.
ESP-14 共接出 22 个接口,ESP-14 贴片式模组的外观尺寸为16mm*24mm *3mm。该模组采用的是容量为1MB, 内置STM8003 MCU和ESP8266 WIFI芯片。ESP8266-14同时支持贴片和DIP插件两种方式,采用2.0的间隔 。
ESP-14 are altogether 18 pin counts, The external size of the module is 16mm *24 mm *3mm .the capacity of which is 1MB.ESP-14 module has a built-in powerful STMs8003F3P6 chips and wifi ESP8266, pick out all the pins, serial port can connected tthe serial port of the ESP8266, users can write STM8 program, through the AT command control WIFI Internet capability.
免费产品试用:
QQ :2154448623
Email :nicole@aithinker.com
Mob:13418538097
P.S.:Manufacturer export please direct contact with nicole@aithinker.com